
Two senior administration officials from Operation Warp Speed offered several updates on COVID-19 vaccine development.

Two senior administration officials from Operation Warp Speed offered several updates on COVID-19 vaccine development.
In a recent interview from Medical Economics, Thomas Ely, DO, discusses how the pandemic is affecting physicians.

In a recent podcast episode from OncLive, Don S. Dizon, MD, FACP, FASCO, discusses the primary physical and residual psychological effects of gynecologic cancers on women’s sexual health.

In July 2019, a jury awarded $229.6 million in the largest medical malpractice verdict ever in the United States.

Senior Editor Angie DeRosa and Associate Editor Lindsey Carr sat down with Drs. Vanessa Rogers and Shawna Nesbitt to discuss racism and unconscious bias in ob/gyn practice.

In the latest issue of Medical Economics, several coding experts give advice on maintaining compliance and collecting revenue for virtual services in the first part of this two-part coding guide.
Results from the study showed antitumor activity and safety to be similar to olaparib and durvalumab monotherapy outcomes.
According to the findings, mammograms declined by 89.2% in April of this year.

Findings from a new study by Australian researchers suggest that physical activity should be incorporated into cancer care during and beyond treatment.

Hear Her aims to raise awareness of pregnancy-related deaths and provide support and education to pregnant women and postpartum women (within 1 year of delivery).
Researchers sought to investigate the effects of endometrioma and the impact of bilaterality on in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) outcomes.
Contemporary OB/GYN Senior Editor Angie DeRosa sat down with Halley Crissman, MD, MPH, and Daphna Stroumsa, MD, MPH, MSC, to discuss gynecologic care considerations for transmasculine people.
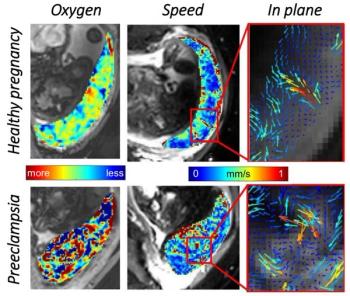
A new study offers important new insights into various placental functions and describes a new physiological phenomenon.

Find additional resources for providing high-quality sexual and reproductive healthcare to transmasculine people, transgender men, and nonbinary people, whose sex assigned at birth was female.

Here’s the latest data, updated on August 14.
The maternal mortality rate for Black mothers is 3 times higher than that of white mothers in the United States.

COVID-19 has brought on plenty of change to all aspects of life, and obstetrics and gynecology is not excluded.

Based on the literature, a bundled intervention was created that included dual antibiotic prophylaxis (cefazolin and metronidazole) aimed at reducing surgical site infections for all patients undergoing hysterectomy.

In this video, Drs. Rogers and Nesbitt break down the differences between equality and equity.
Yesterday, on August 11, 2020, the FDA posted the first spreadsheet of adverse event reports.

There are several steps clinics can take to create a safe, supportive, and welcoming environment for transgender and nonbinary people. Is your hospital and/or practice one of them?

Women who were in the top third of hot flash severity showed a 67% increase in cortisol, whereas those in the bottom third of hot flash severity showed only a 30% increase.
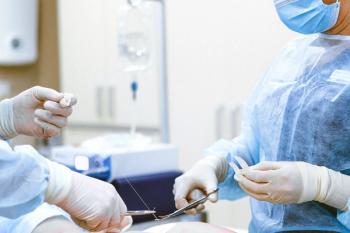
Training gynecologic oncologists to perform cytoreduction for advanced ovarian cancer can result in better outcomes for patients, according to results of a new study

The American College of Physicians (ACP) expressed support for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ (CMS) changes to the Medicare fee schedule.
A literature review in Pediatrics sought to understand more about the possible impacts.

Drs. Rogers and Nesbitt discuss what obstetricians and gynecologists can do to reduce racism and unconscious bias in their practice.
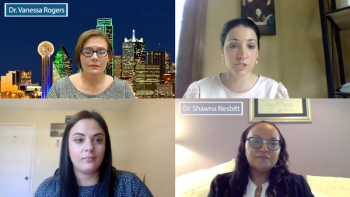
When asked how ob/gyns can make sure diversity and inclusion practices happen in their own practices, Drs. Vanessa Rogers and Shawna Nesbitt of UT Southwestern made it simple.

Transgender and nonbinary people face disproportionate rates of stigma and discrimination in seeking healthcare—and may encounter additional unique barriers in attaining gynecologic and reproductive care.

Transgender and nonbinary people face discrimination and stigma, along with other barriers, in accessing health care.

In a first-of-its-kind report, investigators from New York City have described identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNS in placenta and membrane samples at time of delivery.