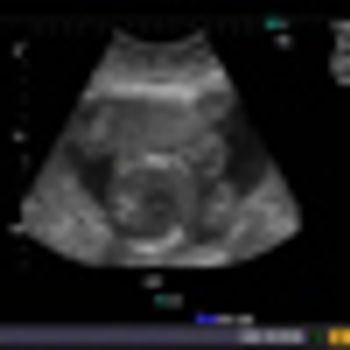
What are echogenic intracardiac foci (EIF)? EIF are small, echogenic lesions seen (on sonography) inside the left or right ventricles of the fetal heart within the papillary muscles or chordae tendinae. These lesions are not attached to the wall of the ventricles.






